Breast Diseases
Breast diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the tissues of the breast. These conditions can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Understanding breast diseases involves knowing the various types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.

Types of Breast Diseases
Breast diseases can be broadly categorized into benign conditions and malignant conditions.
Benign Breast Diseases
Benign breast diseases are non-cancerous conditions and are more common than malignant diseases. They can affect both men and women, though breast diseases are much more common in women. Some common benign breast conditions include:
- Fibrocystic Breast Changes
- Description: A common condition characterized by lumpy, painful breasts, often associated with the menstrual cycle. It is caused by hormonal fluctuations that affect the breast tissue.
- Symptoms: Breast pain or tenderness, lumpiness, and sometimes nipple discharge. Symptoms usually fluctuate with the menstrual cycle and often improve after menstruation.
- Fibroadenomas
- Description: Benign solid tumors that are most common in young women. They are composed of glandular and stromal (connective) tissues and are typically round, firm, and movable.
- Symptoms: A painless, firm, rubbery lump that moves easily under the skin when touched. Usually found in young women aged 15-35.
- Breast Cysts
- Description: Fluid-filled sacs within the breast tissue that can fluctuate in size with the menstrual cycle.
- Symptoms: A round, movable lump that may be tender or painful, especially before menstruation. Cysts are more common in women aged 35-50.
- Intraductal Papilloma
- Description: A small, benign tumor that forms in a milk duct, often near the nipple. It can cause nipple discharge and sometimes a lump.
- Symptoms: Nipple discharge (clear or bloody), a small lump near the nipple, or discomfort.
- Mastitis
- Description: Inflammation of the breast tissue, usually caused by a bacterial infection. It commonly affects breastfeeding women (lactational mastitis) but can occur in non-breastfeeding women (non-lactational mastitis).
- Symptoms: Breast pain, swelling, warmth, redness, fever, and flu-like symptoms. A breast abscess (collection of pus) may develop in severe cases.
- Duct Ectasia
- Description: A benign condition where the milk ducts become widened (dilated) and the duct walls thicken, which can lead to blockage and inflammation.
- Symptoms: Nipple discharge (often thick and greenish), nipple tenderness, or a palpable lump behind the nipple.
- Hyperplasia
- Description: An increase in the number of cells lining the ducts or lobules of the breast. It can be atypical (abnormal cells) or usual (normal cells). Atypical hyperplasia slightly increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Symptoms: Usually asymptomatic and found incidentally during breast biopsies for other reasons.
- Fat Necrosis
- Description: A benign condition resulting from injury to the fatty tissue of the breast, leading to the formation of firm lumps. It can occur after trauma, surgery, or radiation therapy.
- Symptoms: A firm, round lump, sometimes with skin dimpling or redness. It may or may not be painful.
Malignant Breast Diseases (Breast Cancer)
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women worldwide. It occurs when cells in the breast tissue grow uncontrollably and can spread to other parts of the body.
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
- Description: A non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer that starts in the milk ducts and has not spread beyond the duct walls. DCIS is considered the earliest form of breast cancer.
- Symptoms: Usually asymptomatic, but sometimes causes a lump or bloody nipple discharge. Often detected during routine mammograms.
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
- Description: The most common type of breast cancer, starting in the milk ducts and spreading into surrounding breast tissue. It can also metastasize to other parts of the body.
- Symptoms: A lump in the breast, skin changes (dimpling, redness), nipple discharge, or changes in breast shape or size.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)
- Description: The second most common type of invasive breast cancer, starting in the milk-producing lobules and spreading to surrounding tissues.
- Symptoms: A thickening or hardening in the breast, changes in breast texture, or an area of fullness or swelling.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC)
- Description: A rare and aggressive form of breast cancer characterized by the blockage of lymph vessels in the skin of the breast, leading to redness and swelling.
- Symptoms: Red, swollen, and warm breast, often without a distinct lump. The skin may appear pitted like an orange peel (peau d’orange).
- Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
- Description: A type of breast cancer that does not express estrogen receptors (ER), progesterone receptors (PR), or HER2. It tends to be more aggressive and has fewer targeted treatment options.
- Symptoms: Similar to other types of breast cancer but may grow and spread faster.
- HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
- Description: Breast cancer with overexpression of the HER2 protein, which promotes the growth of cancer cells. It tends to be more aggressive but responds well to targeted therapies.
- Symptoms: Symptoms are similar to other breast cancers and depend on the stage of cancer.
- Paget’s Disease of the Breast
- Description: A rare type of cancer involving the skin of the nipple and areola, often associated with underlying DCIS or invasive cancer.
- Symptoms: Scaly, red, itchy, or flaky skin on the nipple and areola, sometimes with nipple discharge.
Causes and Risk Factors of Breast Diseases
Breast diseases have a range of causes and risk factors, which can be divided into modifiable and non-modifiable factors.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Gender: Being female is the most significant risk factor for breast diseases, especially breast cancer.
- Age: The risk of developing breast diseases, particularly breast cancer, increases with age.
- Family History: A family history of breast cancer, especially in a first-degree relative (mother, sister, daughter), increases the risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly increase the risk of breast cancer and other cancers.
- Personal History of Breast Cancer or Certain Benign Breast Conditions: Having breast cancer or certain benign breast conditions, such as atypical hyperplasia, increases the risk of future breast cancer.
- Menstrual and Reproductive History: Early onset of menstruation (before age 12), late menopause (after age 55), and having no children or having the first child after age 30 can increase risk.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of combined hormone therapy (estrogen and progesterone) after menopause increases breast cancer risk.
- Oral Contraceptives: Some studies suggest a slightly increased risk of breast cancer with current or recent use of birth control pills, although the risk decreases after stopping use.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. The risk increases with the amount consumed.
- Obesity and Overweight: Being overweight or obese, especially after menopause, increases the risk of breast cancer due to higher levels of estrogen produced by fat tissue.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of physical activity is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to radiation, particularly during childhood or adolescence, increases breast cancer risk.
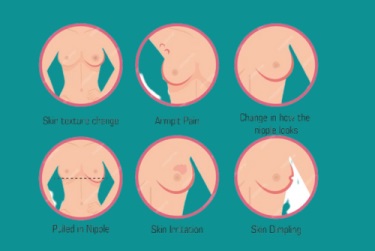
Symptoms of Breast Diseases
Symptoms of breast diseases vary widely depending on the type and severity of the condition:
- Lumps or Masses: A new lump or mass in the breast or underarm is a common symptom. While most breast lumps are benign, they should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Breast Pain or Tenderness: Pain may be associated with benign conditions like fibrocystic changes or infections. Breast cancer is less commonly associated with pain.
- Nipple Discharge: Discharge from the nipple, particularly if it is bloody, clear, or occurs without squeezing the nipple, can indicate an underlying issue.
- Changes in Breast Size or Shape: Unexplained changes in the size or shape of the breast should be evaluated.
- Skin Changes: Redness, dimpling (resembling an orange peel), scaling, or thickening of the breast skin or nipple may indicate a breast disease.
- Nipple Retraction: The nipple turns inward or becomes inverted, which can be a sign of breast cancer.
- Swelling or Thickening: Swelling or thickening of the breast or underarm can be a symptom of various breast diseases.
Diagnosis of Breast Diseases
Diagnosing breast diseases involves a combination of clinical evaluation.
Meet The Breast Specialist Dr. Suhasini Jadhav
Areas We Serve: Kharadi, Viman Nagar, Koregaon Park, Dhanori, Mundhwa, Hadapsar, Lohegaon, Kalyani Nagar, Wagholi, Yerawada, Chandan Nagar, Magarpatta, Wadgaon Sheri, Ubale Nagar, Keshav Nagar, Manjri, Sainikwadi.
Frequently Asked Questions
In Pune, several renowned breast specialists offer comprehensive care for breast-related issues. Dr. Suhasini Jadhav is a highly experienced breast specialist doctor providing expert consultation and treatment for various breast conditions.
Many women feel more comfortable discussing breast health issues with a lady doctor. Dr. Suhasini Jadhav, a trusted lady breast doctor in kharadi, Pune, offers compassionate and confidential care, ensuring patients feel at ease while addressing sensitive concerns.
A breast disease specialist treats various conditions, including breast lumps, cysts, fibrocystic breasts, breast infections, mastitis, and breast cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
You should consult a breast disease doctor if you notice any breast-related symptoms like lumps, persistent pain, nipple discharge, or changes in breast size and shape. Early evaluation by a specialist, such as Dr. Suhasini Jadhav, can help prevent serious complications.
For regular breast check-ups or if you have concerns regarding breast health, consult a breast doctor like Dr. Suhasini Jadhav in Pune. Regular screenings and early detection are key to maintaining good breast health and preventing diseases like breast cancer.
