Lipoma Specialist Doctor in Pune - Dr. Suhasini Jadhav
Lipoma removal is a procedure to remove a lipoma, which is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor composed of fat cells that typically forms under the skin. Lipomas are generally slow-growing, soft, and movable, and they are usually harmless. However, they can sometimes cause discomfort or aesthetic concerns, prompting removal. The decision to remove a lipoma depends on its size, location, symptoms, and patient preference. Here's an in-depth overview of lipomas, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and post-procedure care.
What is a Lipoma?
A lipoma is a soft, fatty lump that grows between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. It is the most common type of soft tissue tumor in adults. Lipomas are usually:
- Soft and Painless: They are typically soft to the touch, easily movable under the skin, and generally not painful unless pressing on nerves or other tissues.
- Slow-Growing: Most lipomas grow slowly over several months or years.
- Small in Size: They are usually small (less than 2 inches in diameter), but they can grow larger.
Causes of Lipomas
The exact cause of lipomas is not well understood, but several factors may contribute to their development:
- Genetic Factors: There appears to be a genetic predisposition to developing lipomas, especially if multiple family members have them. Certain genetic conditions, such as familial multiple lipomatosis, are associated with multiple lipomas.
- Trauma or Injury: Some studies suggest that lipomas may form as a result of an injury that triggers abnormal growth of fat cells, although this is not conclusively proven.
- Age: Lipomas are more common in middle-aged adults (ages 40 to 60) but can occur at any age.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, like Gardner’s syndrome, Madelung’s disease, and adiposis dolorosa, are associated with a higher risk of developing lipomas.
Symptoms of Lipomas
Most lipomas do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Soft, Painless Lump: A lipoma typically feels soft and doughy to the touch and is not tender unless it is pressing on nerves or other structures.
- Mobility: Lipomas are usually easily movable under the skin.
- Size: Lipomas are generally small, but they can grow larger, sometimes reaching up to several inches in diameter.
- Location: Lipomas commonly occur on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, and thighs but can form anywhere on the body.
- Rare Pain or Discomfort: Some lipomas can be painful if they press on nerves or have a lot of blood vessels.
Diagnosis of Lipomas
Diagnosing a lipoma typically involves a physical examination and, in some cases, imaging studies or biopsy:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess the lump’s size, texture, and mobility under the skin. The characteristic features of a lipoma include being soft, non-tender, and easily movable.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies like ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), or CT (computed tomography) scans may be used to confirm the diagnosis, particularly for larger lipomas or those located deeper in the body.
- Biopsy: A biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions, such as liposarcoma (a rare cancerous tumor of fat cells), if the lipoma is unusually large, painful, or has atypical features.
Indications for Lipoma Removal
Lipoma removal is usually considered if the lipoma:
- Becomes Painful or Tender: A lipoma that causes pain or discomfort, particularly if pressing on nerves or muscles.
- Shows Signs of Infection or Inflammation: Although rare, a lipoma can become infected or inflamed, necessitating removal.
- Grows Rapidly: Rapid growth or changes in appearance may warrant removal to rule out malignancy.
- Is Large or Cosmetically Unappealing: Large lipomas or those in visible locations may be removed for cosmetic reasons.
- Causes Functional Impairment: Lipomas that interfere with movement or normal function due to their size or location.
- Has Uncertain Diagnosis: If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, removal and histological examination may be recommended to rule out malignancy.
Methods of Lipoma Removal
The method of lipoma removal depends on the size, location, and characteristics of the lipoma, as well as the patient’s preference.
a. Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is the most common method for removing a lipoma. It involves making an incision over the lipoma and removing it entirely, including its capsule.
1.Procedure:
- The skin over the lipoma is marked and cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
- Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area.
- An incision is made directly over the lipoma.
- The lipoma and its capsule are carefully dissected and removed.
- The incision is closed with sutures, and a sterile dressing is applied.
2. Advantages:
- Complete removal of the lipoma and its capsule reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Provides a sample for histopathological examination to confirm the diagnosis.
3. Risks:
- Scarring, which may be noticeable depending on the size and location of the lipoma.
- Infection, bleeding, or hematoma formation.
- Potential damage to surrounding structures such as nerves or blood vessels.
4. Recovery:
- Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days to a week, depending on the size and location of the lipoma.
- Sutures may need to be removed after 7 to 14 days, depending on the surgical technique used.
b. Minimally Invasive Techniques
Minimally invasive techniques can be used for lipoma removal, especially for smaller lipomas or for patients who prefer less scarring.
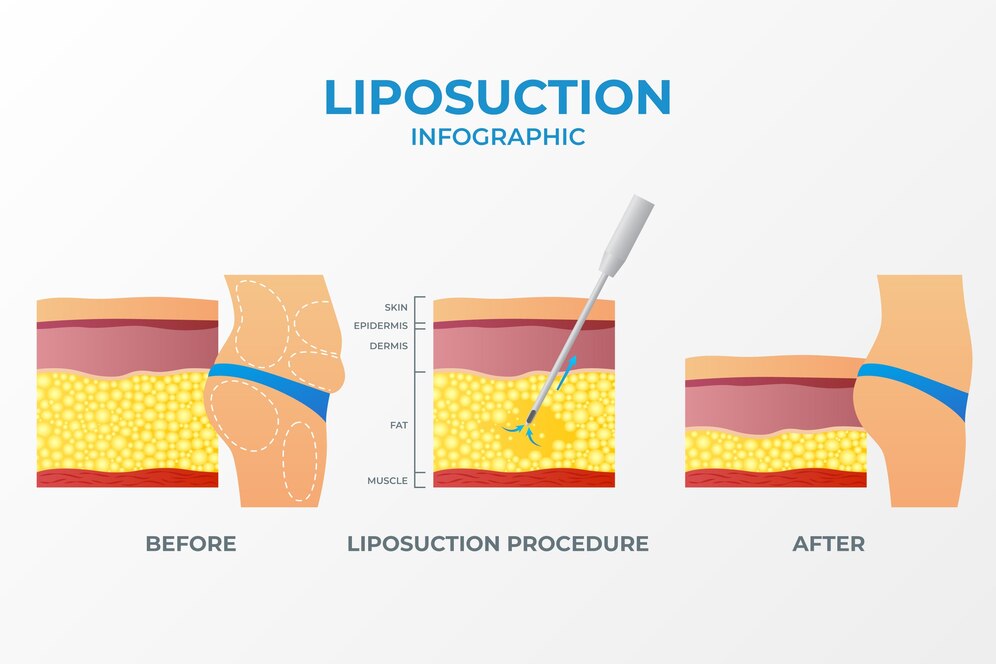
- Liposuction:
- Procedure: Liposuction involves making a small incision and inserting a cannula (a thin, hollow tube) to suction out the fatty tissue.
- Advantages: Smaller incision, less scarring, and quicker recovery.
- Risks: Higher risk of incomplete removal, which may lead to recurrence.
2. Endoscopic Removal:
- Procedure: An endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) is inserted through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to visualize and remove the lipoma with minimal incisions.
- Advantages: Smaller incisions and less scarring, particularly for lipomas located in difficult-to-reach areas.
- Risks: Requires specialized equipment and training, and there may still be a risk of incomplete removal.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before lipoma removal, several steps are taken to ensure a safe and effective procedure:
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical history and physical examination are conducted to assess the lipoma and rule out any contraindications for surgery.
- Imaging Studies: If necessary, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be performed to determine the size, location, and characteristics of the lipoma.
- Preoperative Instructions: Patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, such as blood thinners, and to follow specific instructions regarding eating and drinking before the procedure.
- Informed Consent: The procedure, including potential risks and benefits, will be explained, and informed consent will be obtained.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
Proper post-procedure care is essential for a smooth recovery and to minimize the risk of complications:
- Wound Care: Keep the incision site clean and dry. Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for dressing changes and wound care.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage discomfort. Avoid taking aspirin as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few days to allow the incision to heal properly.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pus, and contact your healthcare provider if these occur.
- Suture Removal: If sutures are used, they are typically removed within 7 to 14 days, depending on the location and size of the lipoma.
Potential Complications
While lipoma removal is generally safe, there are some potential risks and complications:
- Infection: Despite careful wound care, there is a risk of infection, particularly if the lipoma was located in an area prone to contamination.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding is common, but excessive bleeding is rare and may need medical attention.
- Scarring: There may be some scarring at the incision site, which can vary depending on the removal method and individual healing characteristics.
- Hematoma: A collection of blood under the skin (hematoma) can form if there is bleeding during or after the procedure.
- Recurrence: The lipoma may regrow if it is not completely removed, particularly if liposuction is used.
- Nerve Damage: Rarely, there may be temporary or permanent nerve damage, leading to numbness or altered sensation around the incision site.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following
Frequently Asked Questions
The most effective treatment for lipoma is surgical removal, especially if the lipoma is growing, causing discomfort, or affecting appearance. Dr. Suhasini Jadhav, an experienced lipoma specialist in Pune, offers expert diagnosis and personalized treatment plans to safely remove lipomas with minimal scarring.
The cost of lipoma removal surgery in Pune can vary based on factors such as the size, number of lipomas, and the complexity of the procedure. Dr. Suhasini Jadhav provides affordable and transparent pricing for lipoma removal, with personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs.
Dr. Suhasini Jadhav is one of the leading lipoma specialists in Pune, known for her expertise in diagnosing and treating lipomas. With years of experience in handling complex cases, she offers compassionate care and precise surgical interventions to ensure the best outcomes for her patients.
Lipoma surgery with Dr. Suhasini Jadhav ensures safe and effective removal with minimal discomfort and recovery time. She uses advanced techniques to minimize scarring and offers comprehensive post-surgery care to promote quick healing. Patients benefit from personalized attention and expert guidance throughout the treatment process.
Recovery time after lipoma removal surgery is generally quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days. Dr. Suhasini Jadhav provides detailed post-operative care instructions to ensure smooth recovery and follow-up consultations to monitor healing.
